For more examples of using OpenFunction, refer to the samples repository, such as Autoscaling service based on queue depth.
This is the multi-page printable view of this section. Click here to print.
Best Practices
- 1: Create a Knative-based Function to Interact with Middleware
- 2: Use SkyWalking for OpenFunction as an Observability Solution
- 3: Elastic Log Alerting
1 - Create a Knative-based Function to Interact with Middleware
This document describes how to create a Knative-based function to interact with middleware via Dapr components.
Overview
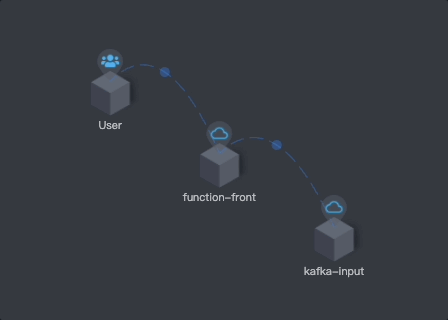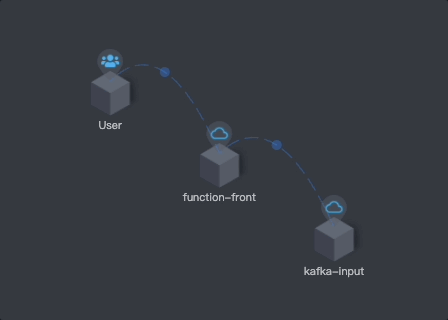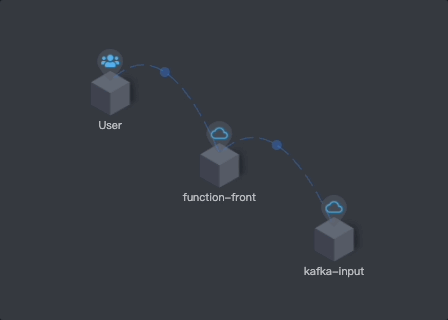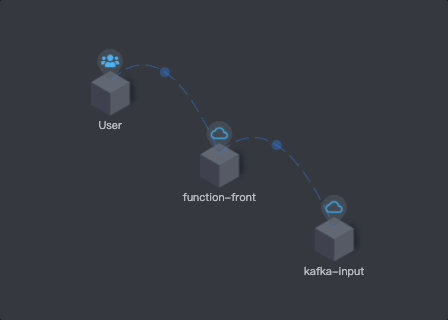
Similar to asynchronous functions, the functions that are based on Knative runtime can interact with middleware through Dapr components. This document uses two functions, function-front and kafka-input, for demonstration.
The following diagram illustrates the relationship between these functions.
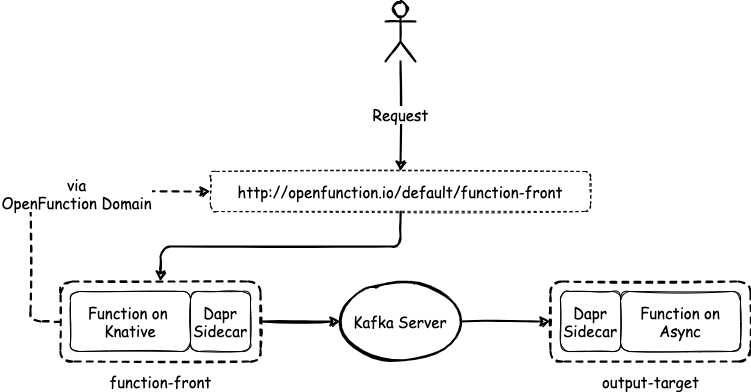
Prerequisites
- You have installed OpenFunction.
- You have created a secret.
Create a Kafka Server and Topic
Run the following commands to install strimzi-kafka-operator in the default namespace.
helm repo add strimzi https://strimzi.io/charts/ helm install kafka-operator -n default strimzi/strimzi-kafka-operatorUse the following content to create a file
kafka.yaml.apiVersion: kafka.strimzi.io/v1beta2 kind: Kafka metadata: name: kafka-server namespace: default spec: kafka: version: 3.3.1 replicas: 1 listeners: - name: plain port: 9092 type: internal tls: false - name: tls port: 9093 type: internal tls: true config: offsets.topic.replication.factor: 1 transaction.state.log.replication.factor: 1 transaction.state.log.min.isr: 1 default.replication.factor: 1 min.insync.replicas: 1 inter.broker.protocol.version: "3.1" storage: type: ephemeral zookeeper: replicas: 1 storage: type: ephemeral entityOperator: topicOperator: {} userOperator: {} --- apiVersion: kafka.strimzi.io/v1beta2 kind: KafkaTopic metadata: name: sample-topic namespace: default labels: strimzi.io/cluster: kafka-server spec: partitions: 10 replicas: 1 config: retention.ms: 7200000 segment.bytes: 1073741824Run the following command to deploy a 1-replica Kafka server named
kafka-serverand 1-replica Kafka topic namedsample-topicin the default namespace.kubectl apply -f kafka.yamlRun the following command to check pod status and wait for Kafka and Zookeeper to be up and running.
$ kubectl get po NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE kafka-server-entity-operator-568957ff84-nmtlw 3/3 Running 0 8m42s kafka-server-kafka-0 1/1 Running 0 9m13s kafka-server-zookeeper-0 1/1 Running 0 9m46s strimzi-cluster-operator-687fdd6f77-cwmgm 1/1 Running 0 11mRun the following commands to view the metadata of the Kafka cluster.
# Starts a utility pod. $ kubectl run utils --image=arunvelsriram/utils -i --tty --rm # Checks metadata of the Kafka cluster. $ kafkacat -L -b kafka-server-kafka-brokers:9092
Create Functions
Use the following example YAML file to create a manifest
kafka-input.yamland modify the value ofspec.imageto set your own image registry address. The fieldspec.serving.inputsdefines an input source that points to a Dapr component of the Kafka server. It means that thekafka-inputfunction will be driven by events in the topicsample-topicof the Kafka server.apiVersion: core.openfunction.io/v1beta2 kind: Function metadata: name: kafka-input spec: version: "v1.0.0" image: <your registry name>/kafka-input:latest imageCredentials: name: push-secret build: builder: openfunction/builder-go:latest env: FUNC_NAME: "HandleKafkaInput" FUNC_CLEAR_SOURCE: "true" srcRepo: url: "https://github.com/OpenFunction/samples.git" sourceSubPath: "functions/async/bindings/kafka-input" revision: "main" serving: scaleOptions: minReplicas: 0 maxReplicas: 10 keda: triggers: - type: kafka metadata: topic: sample-topic bootstrapServers: kafka-server-kafka-brokers.default.svc:9092 consumerGroup: kafka-input lagThreshold: "20" scaledObject: pollingInterval: 15 cooldownPeriod: 60 advanced: horizontalPodAutoscalerConfig: behavior: scaleDown: stabilizationWindowSeconds: 45 policies: - type: Percent value: 50 periodSeconds: 15 scaleUp: stabilizationWindowSeconds: 0 triggers: dapr: - name: target-topic type: bindings.kafka bindings: target-topic: type: bindings.kafka version: v1 metadata: - name: brokers value: "kafka-server-kafka-brokers:9092" - name: topics value: "sample-topic" - name: consumerGroup value: "kafka-input" - name: publishTopic value: "sample-topic" - name: authRequired value: "false" template: containers: - name: function imagePullPolicy: AlwaysRun the following command to create the function
kafka-input.kubectl apply -f kafka-input.yamlUse the following example YAML file to create a manifest
function-front.yamland modify the value ofspec.imageto set your own image registry address.
apiVersion: core.openfunction.io/v1beta2
kind: Function
metadata:
name: function-front
spec:
version: "v1.0.0"
image: "<your registry name>/sample-knative-dapr:latest"
imageCredentials:
name: push-secret
build:
builder: openfunction/builder-go:latest
env:
FUNC_NAME: "ForwardToKafka"
FUNC_CLEAR_SOURCE: "true"
srcRepo:
url: "https://github.com/OpenFunction/samples.git"
sourceSubPath: "functions/knative/with-output-binding"
revision: "main"
serving:
hooks:
pre:
- plugin-custom
- plugin-example
post:
- plugin-example
- plugin-custom
scaleOptions:
minReplicas: 0
maxReplicas: 5
outputs:
- dapr:
name: kafka-server
operation: "create"
bindings:
kafka-server:
type: bindings.kafka
version: v1
metadata:
- name: brokers
value: "kafka-server-kafka-brokers:9092"
- name: authRequired
value: "false"
- name: publishTopic
value: "sample-topic"
- name: topics
value: "sample-topic"
- name: consumerGroup
value: "function-front"
template:
containers:
- name: function
imagePullPolicy: Always
Note
metadata.plugins.pre defines the order of plugins that need to be called before the user function is executed. metadata.plugins.post defines the order of plugins that need to be called after the user function is executed. For more information about the logic of these two plugins and the effect of the plugins after they are executed, see Plugin mechanism.In the manifest,
spec.serving.outputsdefines an output that points to a Dapr component of the Kafka server. That allows you to send custom content to the outputtargetin the functionfunction-front.func Sender(ctx ofctx.Context, in []byte) (ofctx.Out, error) { ... _, err := ctx.Send("target", greeting) ... }Run the following command to create the function
function-front.kubectl apply -f function-front.yaml
Check Results
Run the following command to view the status of the functions.
$ kubectl get functions.core.openfunction.io NAME BUILDSTATE SERVINGSTATE BUILDER SERVING URL AGE function-front Succeeded Running builder-bhbtk serving-vc6jw https://openfunction.io/default/function-front 2m41s kafka-input Succeeded Running builder-dprfd serving-75vrt 2m21sNote
TheURL, provided by the OpenFunction Domain, is the address that can be accessed. To access the function through this URL address, you need to make sure that DNS can resolve this address.Run the following command to create a pod in the cluster for accessing the function.
kubectl run curl --image=radial/busyboxplus:curl -i --tty --rmRun the following command to access the function through
URL.[ root@curl:/ ]$ curl -d '{"message":"Awesome OpenFunction!"}' -H "Content-Type: application/json" -X POST http://openfunction.io.svc.cluster.local/default/function-frontRun the following command to view the log of
function-front.kubectl logs -f \ $(kubectl get po -l \ openfunction.io/serving=$(kubectl get functions function-front -o jsonpath='{.status.serving.resourceRef}') \ -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}') \ functionThe output looks as follows.
dapr client initializing for: 127.0.0.1:50001 I0125 06:51:55.584973 1 framework.go:107] Plugins for pre-hook stage: I0125 06:51:55.585044 1 framework.go:110] - plugin-custom I0125 06:51:55.585052 1 framework.go:110] - plugin-example I0125 06:51:55.585057 1 framework.go:115] Plugins for post-hook stage: I0125 06:51:55.585062 1 framework.go:118] - plugin-custom I0125 06:51:55.585067 1 framework.go:118] - plugin-example I0125 06:51:55.585179 1 knative.go:46] Knative Function serving http: listening on port 8080 2022/01/25 06:52:02 http - Data: {"message":"Awesome OpenFunction!"} I0125 06:52:02.246450 1 plugin-example.go:83] the sum is: 2Run the following command to view the log of
kafka-input.kubectl logs -f \ $(kubectl get po -l \ openfunction.io/serving=$(kubectl get functions kafka-input -o jsonpath='{.status.serving.resourceRef}') \ -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}') \ functionThe output looks as follows.
dapr client initializing for: 127.0.0.1:50001 I0125 06:35:28.332381 1 framework.go:107] Plugins for pre-hook stage: I0125 06:35:28.332863 1 framework.go:115] Plugins for post-hook stage: I0125 06:35:28.333749 1 async.go:39] Async Function serving grpc: listening on port 8080 message from Kafka '{Awesome OpenFunction!}'
2 - Use SkyWalking for OpenFunction as an Observability Solution
This document describes how to use SkyWalking for OpenFunction as an observability solution.
Overview
Although FaaS allows developers to focus on their business code without worrying about the underlying implementations, it is difficult to troubleshoot the service system. OpenFunction tries to introduce capabilities of observability to improve its usability and stability.
SkyWalking provides solutions for observing and monitoring distributed systems in many different scenarios. OpenFunction has bundled go2sky(SkyWalking’s Golang agent) in OpenFunction tracer options to provide distributed tracing, statistics of function performance, and functions dependency map.
Prerequisites
- You have installed OpenFunction.
- You have followed the OpenFunction prerequisites to create a container registry secret, a Kafka cluster and a Kafka topic.
- You have installed SkyWalking v9.
Tracing Parameters
The following table describes the tracing parameters.
| Name | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| enabled | Switch for tracing, default to false. | true, false |
| provider.name | Provider name can be set to “skywalking”, “opentelemetry” (pending). | “skywalking” |
| provider.oapServer | The oap server address. | “skywalking-opa:11800” |
| tags | A collection of key-value pairs for Span custom tags in tracing. | |
| tags.func | The name of function. It will be automatically filled. | “function-a” |
| tags.layer | Indicates the type of service being tracked. It should be set to “faas” when you use the function. | “faas” |
| baggage | A collection of key-value pairs, exists in the tracing and also needs to be transferred across process boundaries. |
The following is a JSON formatted configuration reference that guides the formatting structure of the tracing configuration.
{
"enabled": true,
"provider": {
"name": "skywalking",
"oapServer": "skywalking-oap:11800"
},
"tags": {
"func": "function-a",
"layer": "faas",
"tag1": "value1",
"tag2": "value2"
},
"baggage": {
"key": "key1",
"value": "value1"
}
}
Enable Tracing Configuration of OpenFunction
Option 1: global configuration
This document uses skywalking-oap.default:11800 as an example of the skywalking-oap address in the cluster.
Run the following command to modify the configmap
openfunction-configin theopenfunctionnamespace.kubectl edit configmap openfunction-config -n openfunctionModify the content under
data.plugins.tracingby referring to the following example and save the change.data: tracing: | enabled: true provider: name: "skywalking" oapServer: "skywalking-oap:11800" tags: func: tracing-function layer: faas tag1: value1 tag2: value2 baggage: key: "key1" value: "value1"
Option 2: function-level configuration
To enable tracing configuration in the function-level, add the field plugins.tracing under metadata.annotations in the function manifest as the following example.
metadata:
name: tracing-function
spec:
serving:
tracing:
enabled: true
provider:
name: "skywalking"
oapServer: "skywalking-oap:11800"
tags:
func: tracing-function
layer: faas
tag1: value1
tag2: value2
baggage:
key: "key1"
value: "value1"
It is recommended that you use the global tracing configuration, or you have to add function-level tracing configuration for every function you create.
Use SkyWalking as a Distributed Tracing Solution
Create functions by referring to this document. You can find more examples to create sync and async functions in OpenFunction Quickstarts.
Then, you can observe the flow of entire link on the SkyWalking UI.
You can also observe the comparison of the response time of the Knative runtime function (function-front) in the running state and under cold start.
In cold start:

In running:

3 - Elastic Log Alerting
This document describes how to create an async function to find out error logs.
Overview
This document uses an asynchronous function to analyze the log stream in Kafka to find out the error logs. The async function will then send alerts to Slack. The following diagram illustrates the entire workflow.
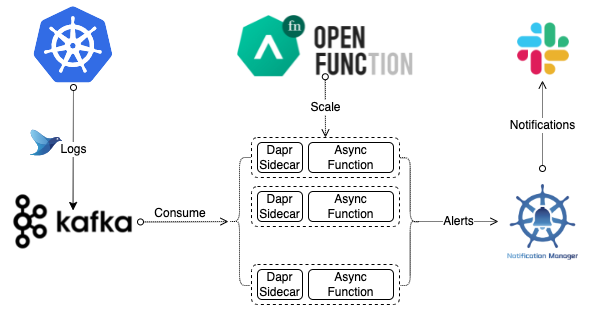
Prerequisites
- You have installed OpenFunction.
- You have created a secret.
Create a Kafka Server and Topic
Run the following commands to install strimzi-kafka-operator in the default namespace.
helm repo add strimzi https://strimzi.io/charts/ helm install kafka-operator -n default strimzi/strimzi-kafka-operatorUse the following content to create a file
kafka.yaml.apiVersion: kafka.strimzi.io/v1beta2 kind: Kafka metadata: name: kafka-logs-receiver namespace: default spec: kafka: version: 3.3.1 replicas: 1 listeners: - name: plain port: 9092 type: internal tls: false - name: tls port: 9093 type: internal tls: true config: offsets.topic.replication.factor: 1 transaction.state.log.replication.factor: 1 transaction.state.log.min.isr: 1 default.replication.factor: 1 min.insync.replicas: 1 inter.broker.protocol.version: "3.1" storage: type: ephemeral zookeeper: replicas: 1 storage: type: ephemeral entityOperator: topicOperator: {} userOperator: {} --- apiVersion: kafka.strimzi.io/v1beta2 kind: KafkaTopic metadata: name: logs namespace: default labels: strimzi.io/cluster: kafka-logs-receiver spec: partitions: 10 replicas: 1 config: retention.ms: 7200000 segment.bytes: 1073741824Run the following command to deploy a 1-replica Kafka server named
kafka-logs-receiverand 1-replica Kafka topic namedlogsin the default namespace.kubectl apply -f kafka.yamlRun the following command to check pod status and wait for Kafka and Zookeeper to be up and running.
$ kubectl get po NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE kafka-logs-receiver-entity-operator-57dc457ccc-tlqqs 3/3 Running 0 8m42s kafka-logs-receiver-kafka-0 1/1 Running 0 9m13s kafka-logs-receiver-zookeeper-0 1/1 Running 0 9m46s strimzi-cluster-operator-687fdd6f77-cwmgm 1/1 Running 0 11mRun the following commands to view the metadata of the Kafka cluster.
# Starts a utility pod. $ kubectl run utils --image=arunvelsriram/utils -i --tty --rm # Checks metadata of the Kafka cluster. $ kafkacat -L -b kafka-logs-receiver-kafka-brokers:9092
Create a Logs Handler Function
- Use the following example YAML file to create a manifest
logs-handler-function.yamland modify the value ofspec.imageto set your own image registry address.
apiVersion: core.openfunction.io/v1beta2
kind: Function
metadata:
name: logs-async-handler
namespace: default
spec:
build:
builder: openfunction/builder-go:latest
env:
FUNC_CLEAR_SOURCE: "true"
FUNC_NAME: LogsHandler
srcRepo:
revision: main
sourceSubPath: functions/async/logs-handler-function/
url: https://github.com/OpenFunction/samples.git
image: openfunctiondev/logs-async-handler:v1
imageCredentials:
name: push-secret
serving:
bindings:
kafka-receiver:
metadata:
- name: brokers
value: kafka-server-kafka-brokers:9092
- name: authRequired
value: "false"
- name: publishTopic
value: logs
- name: topics
value: logs
- name: consumerGroup
value: logs-handler
type: bindings.kafka
version: v1
notification-manager:
metadata:
- name: url
value: http://notification-manager-svc.kubesphere-monitoring-system.svc.cluster.local:19093/api/v2/alerts
type: bindings.http
version: v1
outputs:
- dapr:
name: notification-manager
operation: post
type: bindings.http
scaleOptions:
keda:
scaledObject:
advanced:
horizontalPodAutoscalerConfig:
behavior:
scaleDown:
policies:
- periodSeconds: 15
type: Percent
value: 50
stabilizationWindowSeconds: 45
scaleUp:
stabilizationWindowSeconds: 0
cooldownPeriod: 60
pollingInterval: 15
triggers:
- metadata:
bootstrapServers: kafka-server-kafka-brokers.default.svc.cluster.local:9092
consumerGroup: logs-handler
lagThreshold: "20"
topic: logs
type: kafka
maxReplicas: 10
minReplicas: 0
template:
containers:
- imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
name: function
triggers:
dapr:
- name: kafka-receiver
type: bindings.kafka
workloadType: Deployment
version: v2.0.0
workloadRuntime: OCIContainer
Run the following command to create the function
logs-async-handler.kubectl apply -f logs-handler-function.yamlThe logs handler function will be triggered by messages from the logs topic in Kafka.