This is the multi-page printable view of this section. Click here to print.
Networking
1 - Introduction
Overview
Previously starting from v0.5.0, OpenFunction uses Kubernetes Ingress to provide unified entrypoints for sync functions, and a nginx ingress controller has to be installed.
With the maturity of Kubernetes Gateway API, we decided to implement OpenFunction Gateway based on the Kubernetes Gateway API to replace the previous ingress based domain method in OpenFunction v0.7.0.
You can find the OpenFunction Gateway proposal here
OpenFunction Gateway provides a more powerful and more flexible function gateway including features like:
Enable users to switch to any gateway implementations that support Kubernetes Gateway API such as Contour, Istio, Apache APISIX, Envoy Gateway (in the future) and more in an easier and vendor-neutral way.
Users can choose to install a default gateway implementation (Contour) and then define a new
gateway.networking.k8s.ioor use any existing gateway implementations in their environment and then reference an existinggateway.networking.k8s.io.Allow users to customize their own function access pattern like
hostTemplate: "{{.Name}}.{{.Namespace}}.{{.Domain}}"for host-based access.Allow users to customize their own function access pattern like
pathTemplate: "{{.Namespace}}/{{.Name}}"for path-based access.Allow users to customize each function’s route rules (host-based, path-based or both) in function definition and default route rules are provided for each function if there’re no customized route rules defined.
Send traffic to Knative service revisions directly without going through Knative’s own gateway anymore. You will need only OpenFunction Gateway since OpenFunction 0.7.0 to access OpenFunction sync functions, and you can ignore Knative’s domain config errors if you do not need to access Knative service directly.
Traffic splitting between function revisions (in the future)
The following diagram illustrates how client traffics go through OpenFunction Gateway and then reach a function directly:
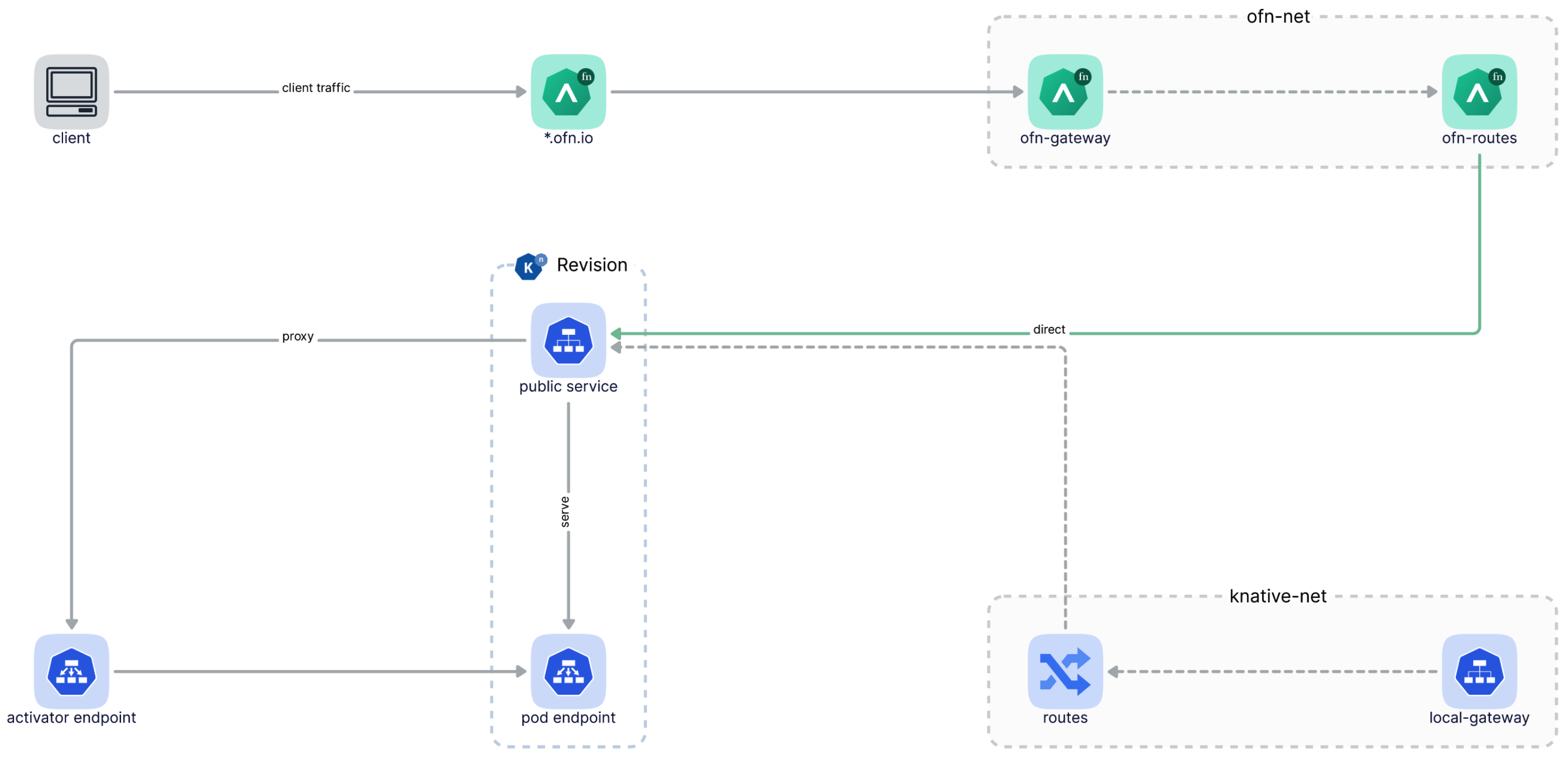
2 - OpenFunction Gateway
Inside OpenFunction Gateway
Backed by the Kubernetes Gateway, an OpenFunction Gateway defines how users can access sync functions.
Whenever an OpenFunction Gateway is created, the gateway controller will:
Add a default listener named
ofn-http-internaltogatewaySpec.listenersif there isn’t one there.Generate
gatewaySpec.listeners.[*].hostnamebased ondomainorclusterDomain.Inject
gatewaySpec.listentersto the existingKubernetes Gatewaydefined by thegatewayRefof theOpenFunction Gateway.Create an new
Kubernetes Gatewaybased on thegatewaySpec.listentersfield ingatewayDefof theOpenFunction Gateway.Create a service named
gateway.openfunction.svc.cluster.localthat defines a unified entry for sync functions.
After an OpenFunction Gateway is deployed, you’ll be able to find the status of Kubernetes Gateway and its listeners in OpenFunction Gateway status:
status:
conditions:
- message: Gateway is scheduled
reason: Scheduled
status: "True"
type: Scheduled
- message: Valid Gateway
reason: Valid
status: "True"
type: Ready
listeners:
- attachedRoutes: 0
conditions:
- message: Valid listener
reason: Ready
status: "True"
type: Ready
name: ofn-http-internal
supportedKinds:
- group: gateway.networking.k8s.io
kind: HTTPRoute
- attachedRoutes: 0
conditions:
- message: Valid listener
reason: Ready
status: "True"
type: Ready
name: ofn-http-external
supportedKinds:
- group: gateway.networking.k8s.io
kind: HTTPRoute
The Default OpenFunction Gateway
OpenFunction Gateway uses Contour as the default Kubernetes Gateway implementation.
The following OpenFunction Gateway will be created automatically once you install OpenFunction:
apiVersion: networking.openfunction.io/v1alpha1
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: openfunction
namespace: openfunction
spec:
domain: ofn.io
clusterDomain: cluster.local
hostTemplate: "{{.Name}}.{{.Namespace}}.{{.Domain}}"
pathTemplate: "{{.Namespace}}/{{.Name}}"
httpRouteLabelKey: "app.kubernetes.io/managed-by"
gatewayRef:
name: contour
namespace: projectcontour
gatewaySpec:
listeners:
- name: ofn-http-internal
hostname: "*.cluster.local"
protocol: HTTP
port: 80
allowedRoutes:
namespaces:
from: All
- name: ofn-http-external
hostname: "*.ofn.io"
protocol: HTTP
port: 80
allowedRoutes:
namespaces:
from: All
You can customize the default OpenFunction Gateway like below:
kubectl edit gateway openfunction -n openfunction
Switch to a different Kubernetes Gateway
You can switch to any gateway implementations that support Kubernetes Gateway API such as Contour, Istio, Apache APISIX, Envoy Gateway (in the future) and more in an easier and vendor-neutral way.
Here you can find more details.
Multiple OpenFunction Gateway
Multiple Gateway are meaningless for OpenFunction, we currently only support one OpenFunction Gateway.
3 - Route
What is Route?
Route is part of the Function definition. Route defines how traffic from the Gateway listener is routed to a function.
A Route specifies the Gateway to which it will attach in GatewayRef that allows it to receive traffic from the Gateway.
Once a sync Function is created, the function controller will:
- Look for the
Gatewaycalledopenfunctioninopenfunctionnamespace, then attach to thisGatewayifroute.gatewayRefis not defined in the function. - Automatically generate
route.hostnamesbased onGateway.spec.hostTemplate, ifroute.hostnamesis not defined in function. - Automatically generate
route.rulesbased onGateway.spec.pathTemplateor path of/, ifroute.rulesis not defined in function. - a
HTTPRoutecustom resource will be created based onRoute.BackendRefswill be automatically link to the corresponding Knative service revision and labelHTTPRouteLabelKeywill be added to thisHTTPRoute. - Create service
{{.Name}}.{{.Namespace}}.svc.cluster.local, this service defines an entry for the function to access within the cluster. - If the
Gatewayreferenced byroute.gatewayRefchanged, will update theHTTPRoute.
After a sync Function is deployed, you’ll be able to find Function addresses and Route status in Function’s status field, e.g:
status:
addresses:
- type: External
value: http://function-sample-serving-only.default.ofn.io/
- type: Internal
value: http://function-sample-serving-only.default.svc.cluster.local/
build:
resourceHash: "14903236521345556383"
state: Skipped
route:
conditions:
- message: Valid HTTPRoute
reason: Valid
status: "True"
type: Accepted
hosts:
- function-sample-serving-only.default.ofn.io
- function-sample-serving-only.default.svc.cluster.local
paths:
- type: PathPrefix
value: /
serving:
lastSuccessfulResourceRef: serving-znk54
resourceHash: "10715302888241374768"
resourceRef: serving-znk54
service: serving-znk54-ksvc-nbg6f
state: Running
Note
The Address of type Internal in Funtion.status provides the default method for accessing functions from within the cluster.
This internal address is not affected by the Gateway referenced by route.gatewayRef and it’s suitable for use as sink.url of EventSource.
The Address of type External in Funtion.status provides methods for accessing functions from outside the cluster (You can choose to configure Magic DNS or real DNS, please refer to access functions by the external address for more details).
This external address is generated based on route.gatewayRef, router.hostnames and route.rules. The routing mode only takes effect on this external address, The following documentation will explain how it works.
For more information about how to access functions, please refer to Function Entrypoints.
Host Based Routing
Host-based is the default routing mode. When route.hostnames is not defined,
route.hostnames will be generated based on gateway.spec.hostTemplate.
If route.rules is not defined, route.rules will be generated based on path of /.
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: core.openfunction.io/v1beta2
kind: Function
metadata:
name: function-sample
spec:
version: "v1.0.0"
image: "openfunctiondev/v1beta1-http:latest"
serving:
template:
containers:
- name: function
imagePullPolicy: Always
triggers:
http:
route:
gatewayRef:
name: openfunction
namespace: openfunction
EOF
If you are using the default OpenFunction Gateway, the function external address will be as below:
http://function-sample.default.ofn.io/
Path Based Routing
If you define route.hostnames in a function, route.rules will be generated based on gateway.spec.pathTemplate.
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: core.openfunction.io/v1beta2
kind: Function
metadata:
name: function-sample
spec:
version: "v1.0.0"
image: "openfunctiondev/v1beta1-http:latest"
serving:
template:
containers:
- name: function
imagePullPolicy: Always
triggers:
http:
route:
gatewayRef:
name: openfunction
namespace: openfunction
hostnames:
- "sample.ofn.io"
EOF
If you are using the default OpenFunction Gateway, the function external address will be as below:
http://sample.default.ofn.io/default/function-sample/
Host and Path based routing
You can define hostname and path at the same time to customize how traffic should be routed to your function.
Note
In this mode, you’ll need to resolve possible conflicts between HTTPRoutes by yourself.kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: core.openfunction.io/v1beta2
kind: Function
metadata:
name: function-sample
spec:
version: "v1.0.0"
image: "openfunctiondev/v1beta1-http:latest"
serving:
template:
containers:
- name: function
imagePullPolicy: Always
triggers:
http:
route:
gatewayRef:
name: openfunction
namespace: openfunction
rules:
- matches:
- path:
type: PathPrefix
value: /v2/foo
hostnames:
- "sample.ofn.io"
EOF
If you are using the default OpenFunction Gateway, the function external address will be as below:
http://sample.default.ofn.io/v2/foo/
4 - Function Entrypoints
There are several methods to access a sync function. Let’s elaborate on this in the following section.
This documentation will assume you are using default OpenFunction Gateway and you have a sync function named
function-sample.
Access functions from within the cluster
Access functions by the internal address
OpenFunction will create this service for every sync Function: {{.Name}}.{{.Namespace}}.svc.cluster.local. This service will be used to provide the Function internal address.
Get Function internal address by running following command:
export FUNC_INTERNAL_ADDRESS=$(kubectl get function function-sample -o=jsonpath='{.status.addresses[?(@.type=="Internal")].value}')
This address provides the default method for accessing functions within the cluster, it’s suitable for use as sink.url of EventSource.
Access Function using curl in pod:
kubectl run --rm ofn-test -i --tty --image=radial/busyboxplus:curl -- curl -sv $FUNC_INTERNAL_ADDRESS
Access functions from outside the cluster
Access functions by the Kubernetes Gateway’s IP address
Get Kubernetes Gateway’s ip address:
export IP=$(kubectl get node -l "! node.kubernetes.io/exclude-from-external-load-balancers" -o=jsonpath='{.items[0].status.addresses[?(@.type=="InternalIP")].address}')
Get Function’s HOST and PATH:
export FUNC_HOST=$(kubectl get function function-sample -o=jsonpath='{.status.route.hosts[0]}')
export FUNC_PATH=$(kubectl get function function-sample -o=jsonpath='{.status.route.paths[0].value}')
Access Function using curl directly:
curl -sv -HHOST:$FUNC_HOST http://$IP$FUNC_PATH
Access functions by the external address
To access a sync function by the external address, you’ll need to configure DNS first. Either Magic DNS or real DNS works:
Magic DNS
Get Kubernetes Gateway’s ip address:
export IP=$(kubectl get node -l "! node.kubernetes.io/exclude-from-external-load-balancers" -o=jsonpath='{.items[0].status.addresses[?(@.type=="InternalIP")].address}')Replace domain defined in OpenFunction Gateway with Magic DNS:
export DOMAIN="$IP.sslip.io" kubectl patch gateway.networking.openfunction.io/openfunction -n openfunction --type merge --patch '{"spec": {"domain": "'$DOMAIN'"}}'Then, you can see
Functionexternal address inFunction’s status field:kubectl get function function-sample -oyamlstatus: addresses: - type: External value: http://function-sample.default.172.31.73.53.sslip.io/ - type: Internal value: http://function-sample.default.svc.cluster.local/ build: resourceHash: "14903236521345556383" state: Skipped route: conditions: - message: Valid HTTPRoute reason: Valid status: "True" type: Accepted hosts: - function-sample.default.172.31.73.53.sslip.io - function-sample.default.svc.cluster.local paths: - type: PathPrefix value: / serving: lastSuccessfulResourceRef: serving-t56fq resourceHash: "2638289828407595605" resourceRef: serving-t56fq service: serving-t56fq-ksvc-bv8ng state: RunningReal DNS
If you have an external IP address, you can configure a wildcard A record as your domain:
# Here example.com is the domain defined in OpenFunction Gateway *.example.com == A <external-ip>If you have a CNAME, you can configure a CNAME record as your domain:
# Here example.com is the domain defined in OpenFunction Gateway *.example.com == CNAME <external-name>Replace domain defined in OpenFunction Gateway with the domain you configured above:
export DOMAIN="example.com" kubectl patch gateway.networking.openfunction.io/openfunction -n openfunction --type merge --patch '{"spec": {"domain": "'$DOMAIN'"}}'Then, you can see
Functionexternal address inFunction’s status field:kubectl get function function-sample -oyamlstatus: addresses: - type: External value: http://function-sample.default.example.com/ - type: Internal value: http://function-sample.default.svc.cluster.local/ build: resourceHash: "14903236521345556383" state: Skipped route: conditions: - message: Valid HTTPRoute reason: Valid status: "True" type: Accepted hosts: - function-sample.default.example.com - function-sample.default.svc.cluster.local paths: - type: PathPrefix value: / serving: lastSuccessfulResourceRef: serving-t56fq resourceHash: "2638289828407595605" resourceRef: serving-t56fq service: serving-t56fq-ksvc-bv8ng state: Running
Then, you can get Function external address by running following command:
export FUNC_EXTERNAL_ADDRESS=$(kubectl get function function-sample -o=jsonpath='{.status.addresses[?(@.type=="External")].value}')
Now, you can access Function using curl directly:
curl -sv $FUNC_EXTERNAL_ADDRESS